 UCROPS Workflow
UCROPS Workflow
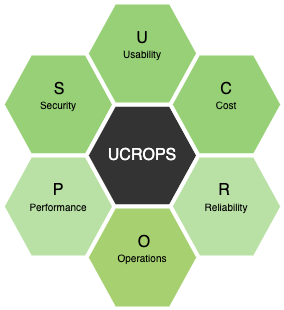
UCROPS
Tips
- UCROPS Well-Architected framework is used to:
- evaluate and compare pros/cons of each service
- evaluate the pros/cons of our overall architecture plans
- research alternatives given these criteria
- describe our solutions in an organized way
- U - Usability
- C - Cost
- R - Reliability
- O - Operations
- P - Performance
- S - Security
Usability
A bit of a catch-all, and also the ultimate goal.
- Fits the usability needs of all User Roles.
- User interface easy-to-use and responsive.
- Admin interface easy-to-use use.
- Easily understandable UI for users, codebase for devs.
- Documentation complete and resolves many issues.
- Lower complexity is better.
- Lower tech dependencies is better.
- Accessibility.
"Understandability"... According to Google SRE book Building Secure and Reliable Systems, Understandability is a key component of reliability:
- "Reliability and security benefit, in a deep and intertwined way, from understandable systems."
- Decreases security vulnerabilities or resilience failures
- Facilitates effective incident response
- Increases confidence in assertions about a system’s security posture
- Increased likelihood that the resulting system is actually correct
- Structured interfaces, consistent object models, and idempotent operations contrib‐ ute to a system’s understandability
- Code readability and auditability
Cost
- Selecting resources of the right type and quantity,
- Scaling to meet business needs without overspending.
- Cloud financial management
- Projecting spending over time,
- Controlling fund allocation
Reliability
- Distributed system design
- High Availability, Reliability, Fault Tolerance
- Time and Request-based Availability
- Workloads performing their intended functions
- Fault-tolerance, recover quickly from failure
- Detect, Handle, Recover from partial failures
- Types of failure: Crash, Timeout, Response, Incorrect response, Arbitrary response
- Disaster Recovery planning,
- Backup
- CAP Theorem
- Reliability testing
- Adapting to changing requirements
Operations
- Infrastructure as code
- DevOps Automate changes,
- Respond quickly to events,
- Monitor systems,
- Continuous improvements
- Defining standards to manage daily operations.
- Define organizational requirements
Performance
- Select optimized resources for workload,
- Optimize all parts and the whole of the stack
- Monitor performance
- Maintain efficiency
- Resolve performance issues
Security
- IAM/account security, roles for access
- Encryption/security at rest
- Encryption/security in transit
- Network, perimeter security
- Violation resolution process